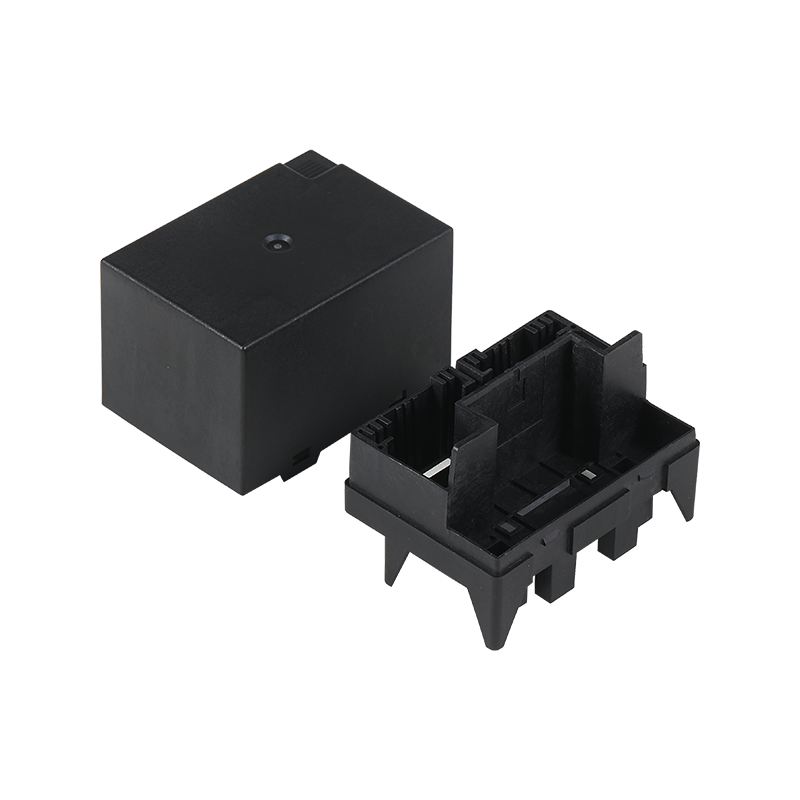
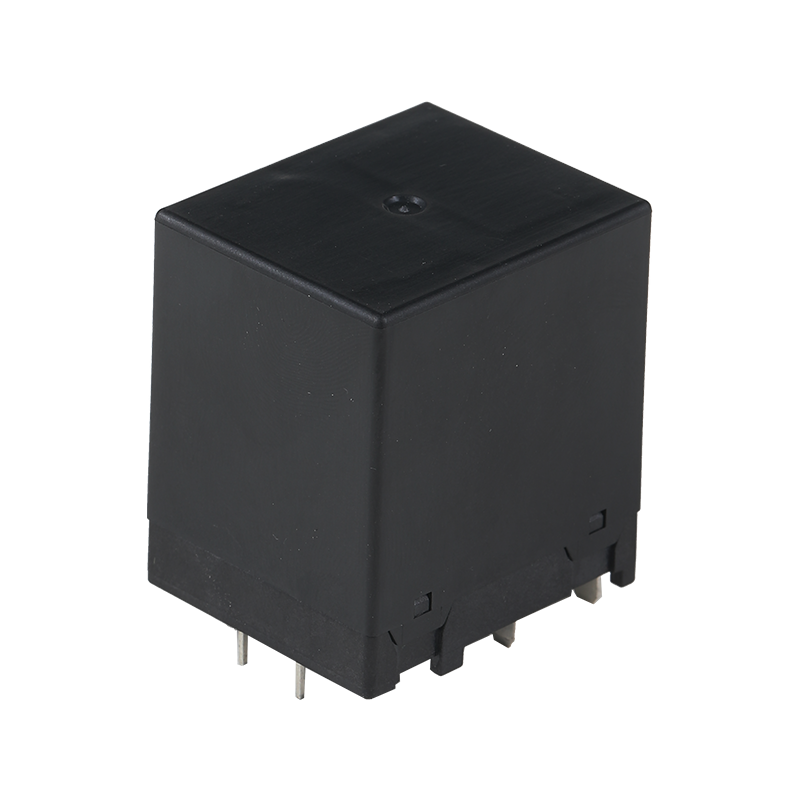
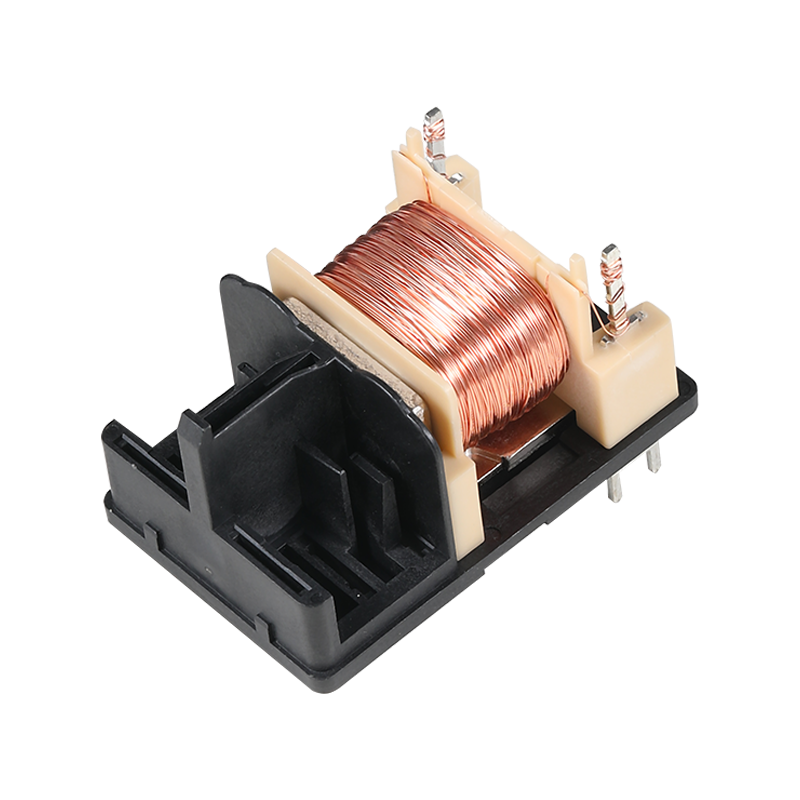
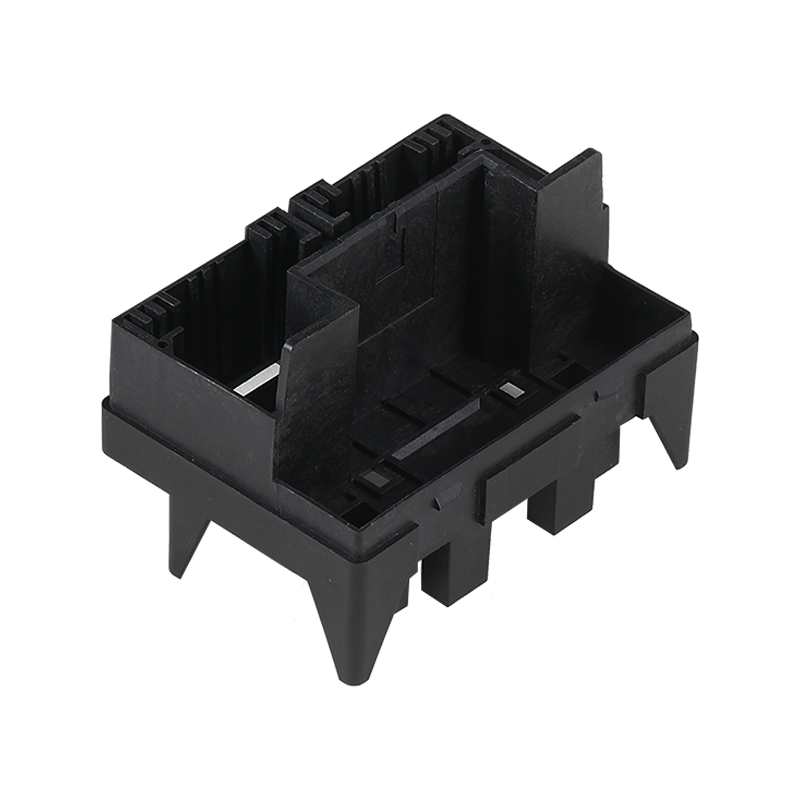
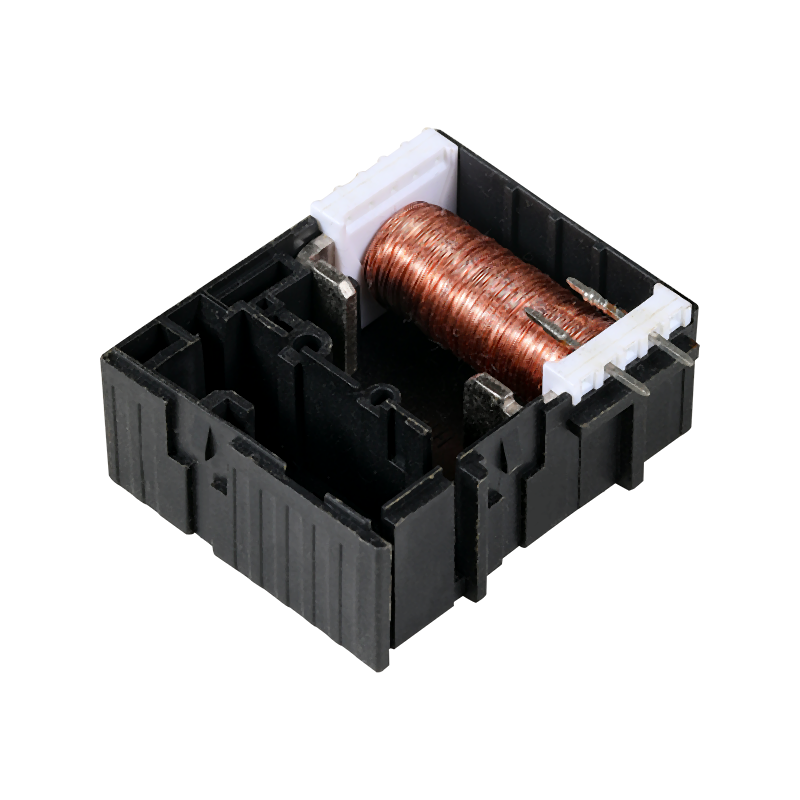
ABS (Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene) plastic is a popular thermoplastic material known for its strength, durability, and versatility. It is widely used in various industries due to its unique combination of properties.
Heat molding is a manufacturing process that involves shaping materials, such as ABS plastic, by applying heat and pressure. In the case of ABS, heat molding allows the material to be transformed into a desired shape or form. The process begins with the material being heated to a specific temperature, which is above its glass transition temperature but below its melting point. This allows the ABS plastic to become pliable and moldable without losing its structural integrity.
Once the ABS plastic reaches the appropriate temperature, it is placed into a mold. The mold is designed to have the exact shape and detail of the final product. Pressure is then applied to force the ABS plastic into the mold's cavity. As the plastic cools, it hardens and takes on the shape of the mold. This process can be used to create a wide range of products, from automotive parts to consumer electronics.
The moldability of ABS plastic is one of its more significant advantages. It can be easily shaped and molded into complex forms with fine details. This is due to the material's blend of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, which contribute to its toughness, flexibility, and rigidity, respectively. The balance of these properties allows ABS to be both strong and impact-resistant while also being easy to work with during the molding process.
ABS plastic's moldability also extends to its ability to be colored and finished in various ways. It can be easily dyed or painted, and it can accept a wide range of surface treatments, such as plating, metallization, and texturing. This versatility makes ABS an ideal material for products that require both functional and aesthetic considerations.
The quality of the final product depends largely on the design and manufacture of the mold. ABS molds must be precisely manufactured to ensure that the shape and details of the final product are accurate. Mold design is a complex process that requires consideration of product geometry, draft angles, cooling systems, and material flow paths. High-quality molds can increase production efficiency, reduce scrap rates, and ensure product consistency.
ABS molds are usually made of steel, a material favored for its durability and strength. The surface treatment of the mold is also important because it can affect the demolding of the plastic and the surface quality of the final product. Common surface treatments include polishing, coating, and electroplating, which can improve the wear and corrosion resistance of the mold and extend its service life.
ABS plastic finds applications in a multitude of industries due to its heat resistance, rigidity, and impact resistance. In the automotive industry, it is used for making body panels, dashboards, and interior components. In consumer electronics, ABS is used for housings of devices like computers, televisions, and mobile phones. Its versatility also makes it suitable for toys, furniture, and even the construction of musical instruments.
While ABS plastic offers many benefits, it is essential to consider its environmental impact. ABS is not biodegradable and can contribute to plastic waste if not properly managed. Recycling ABS can help mitigate this issue, and many recycling programs accept ABS as a recyclable material. However, the recycling process can be complex due to the material's blend of polymers, and not all recycling facilities may be equipped to handle it.
In conclusion, ABS plastic is a versatile and robust material that is well-suited for heat molding and molding processes. Its moldability and the precision of ABS molds are critical factors in the production of high-quality products across various industries.
 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский