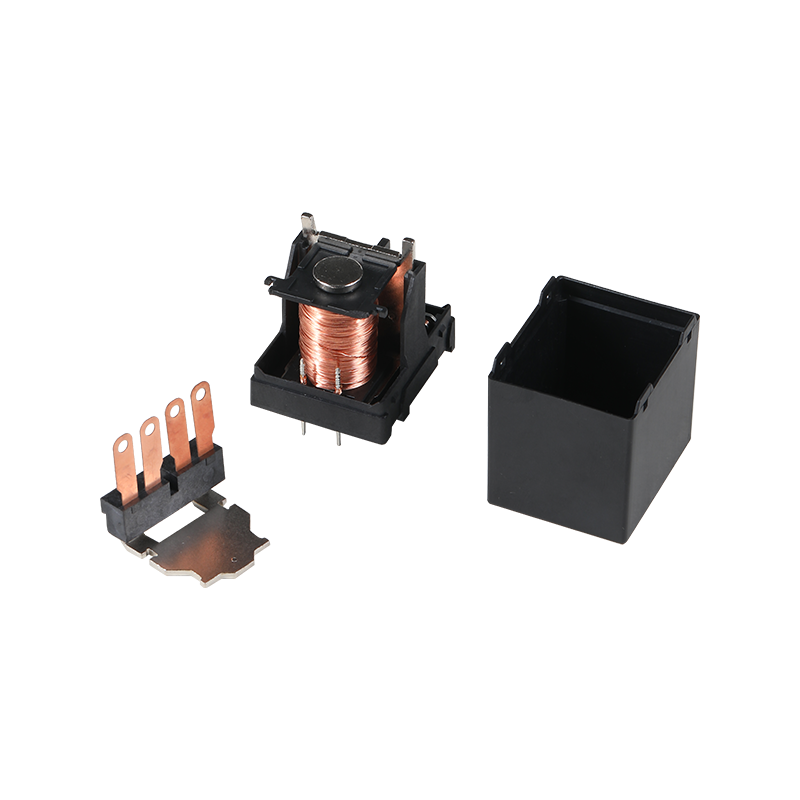
Plastic molding is a widely used manufacturing process, with applications spanning various industries, including automotive, electronics, and household products. These molds are specifically designed to shape plastic materials into the desired final product, ensuring consistency and quality in mass production.
A case plastic mold is a type of injection mold that is used to create cases or enclosures for various products. These molds are typically made from high-strength metals such as steel or aluminum to withstand the high pressures and temperatures involved in the injection molding process. The mold consists of two halves – the cavity and the core – which work together to form the plastic part. The cavity is where the molten plastic is injected, and the core shapes the inner features of the molded case.
Case plastic molds are used to produce a wide range of products, including protective enclosures for electronic devices, housing for automotive parts, and containers for industrial use. The design and material choices of the mold are essential to the performance and durability of the final plastic product.
The creation of a case plastic mold follows several key steps, which include:
Design and Prototyping: The one step in creating a case plastic mold is designing the product and the mold itself. Designers use computer-aided design (CAD) software to create a 3D model of the case, considering factors such as ease of assembly, material flow, and moldability. Prototypes are often made to test the design before the final mold is created.
Mold Fabrication: Once the design is finalized, the next step is to fabricate the mold. This process often involves precision machining, such as milling, drilling, and EDM (electrical discharge machining) to create the cavity and core. The mold is then polished to ensure smooth surfaces and small imgoodions in the final product.
Injection Molding: After the mold is prepared, the injection molding process begins. In this step, plastic pellets are heated until they melt and are injected into the mold under high pressure. The molten plastic fills the cavity, taking the shape of the case. Once the plastic cools and hardens, the mold is opened, and the case is ejected.
Post-Processing: Depending on the requirements of the product, additional steps such as trimming, surface finishing, or assembly may be needed to complete the molded case.
Advantages of Using Case Plastic Molds:
Precision and Consistency: Case plastic molds ensure high precision and consistency in the production of plastic components. This is especially important in industries where the accuracy of the molded cases is crucial, such as in electronics and automotive applications.
Versatility in Material Selection: Case plastic molds can accommodate a wide variety of plastic materials, including thermoplastics and thermosets. This versatility makes them suitable for different types of products and industries.
Durability: The molds are designed to withstand the pressure and temperature of the injection molding process, ensuring that they last for a significant number of cycles. This durability makes case plastic molds a reliable option for long-term production.
Case plastic molds are a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling the production of high-quality, cost-effective plastic components. Their ability to produce complex shapes with high precision, along with the versatility to work with various materials, makes them indispensable in many industries.
 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский








