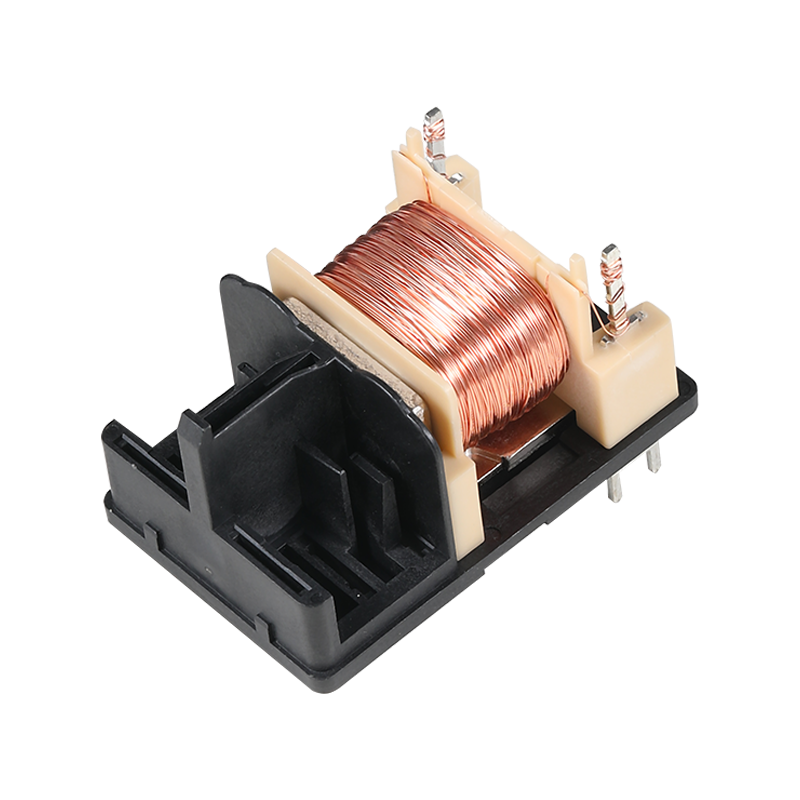
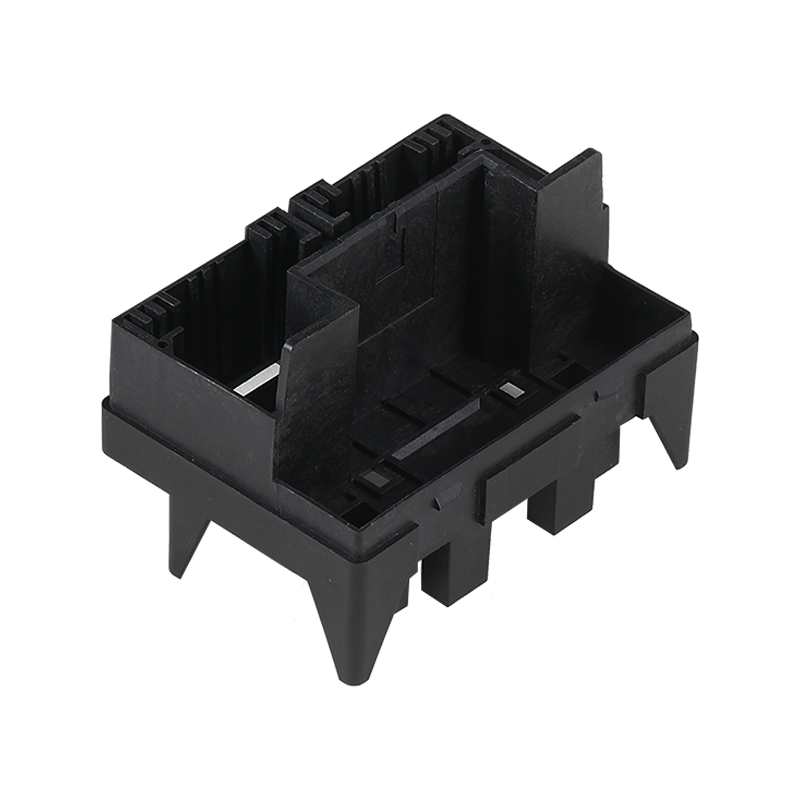
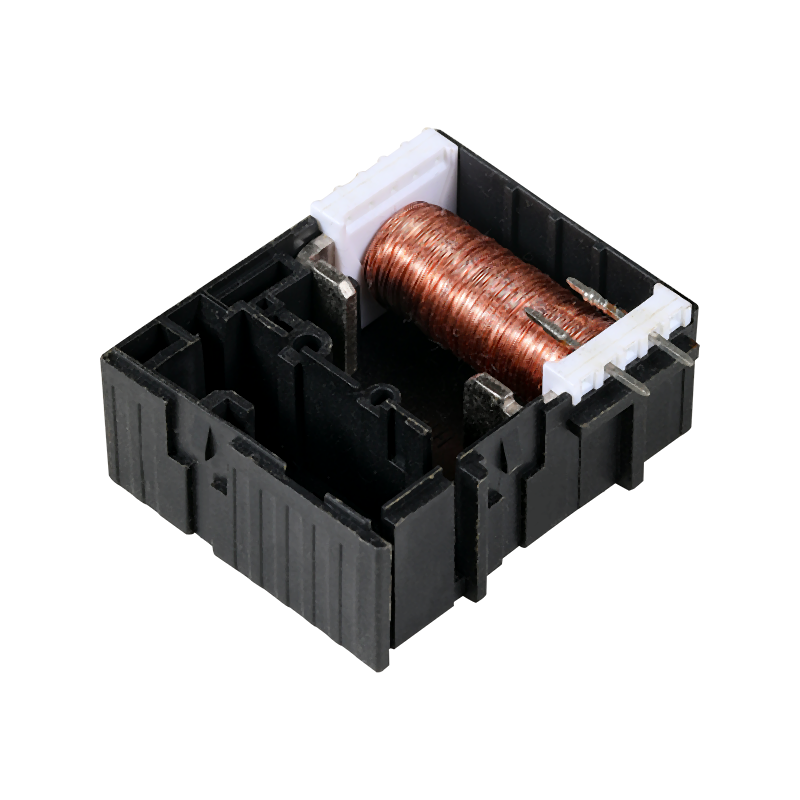
Prototype molding plastic is a process that allows designers and engineers to test and good their designs before committing to large-scale production.
Prototype molding plastic is a critical step in the product development cycle. It involves creating a physical model of a design using plastic materials, which can then be tested for functionality, aesthetics, and durability. This process is essential for identifying any issues with the design before it moves into mass production, saving both time and resources. Prototypes can be made from a variety of plastics, each with its own set of properties that can mimic the final product's material characteristics.
The use of prototype molding allows for iterative design processes, where multiple versions of a product can be created and tested. This iterative approach is fundamental in refining the design to meet specific performance criteria, ensuring that the final product is both functional and market-ready. Prototypes can also be used for marketing purposes, providing a tangible representation of the product to potential investors or customers.
Flexible injection molded plastics are a subset of injection molding that utilizes materials with elastic properties. These materials can be stretched and flexed without breaking, making them ideal for applications where flexibility is required. The flexibility of these plastics allows for the creation of complex shapes and designs that would be impossible with rigid materials.
The process of injection molding involves injecting molten plastic material into a mold, where it cools and hardens to take the shape of the mold cavity. Flexible injection molded plastics offer a high degree of design freedom, as they can be engineered to have specific levels of flexibility and durability. This adaptability makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to automotive components.
Low volume plastic parts are produced in smaller quantities, often for specialized applications or niche markets. These parts may require intricate detailing or specific material properties that are not feasible in high-volume production runs. The production of low volume plastic parts allows for greater customization and precision, as manufacturers can focus on the quality and intricacy of each individual piece.
The demand for low volume plastic parts is driven by industries that require specialized components, such as medical devices, aerospace, and high-end consumer goods. These parts often need to meet stringent quality control standards and may incorporate advanced materials or complex geometries. The ability to produce these parts in low volumes allows manufacturers to cater to the specific needs of their clients without the overhead associated with mass production.
The combination of prototype molding plastic, flexible injection molded plastics, and low volume plastic parts represents the future of plastics manufacturing. These processes enable innovation, flexibility, and precision, catering to the diverse needs of modern industries. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even greater developments in the field of plastics manufacturing, with prototype molding playing a central role in the evolution of new products and materials. The ability to quickly and accurately produce prototypes will remain a cornerstone of product development, ensuring that the plastics industry remains at the forefront of innovation and efficiency.
 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский