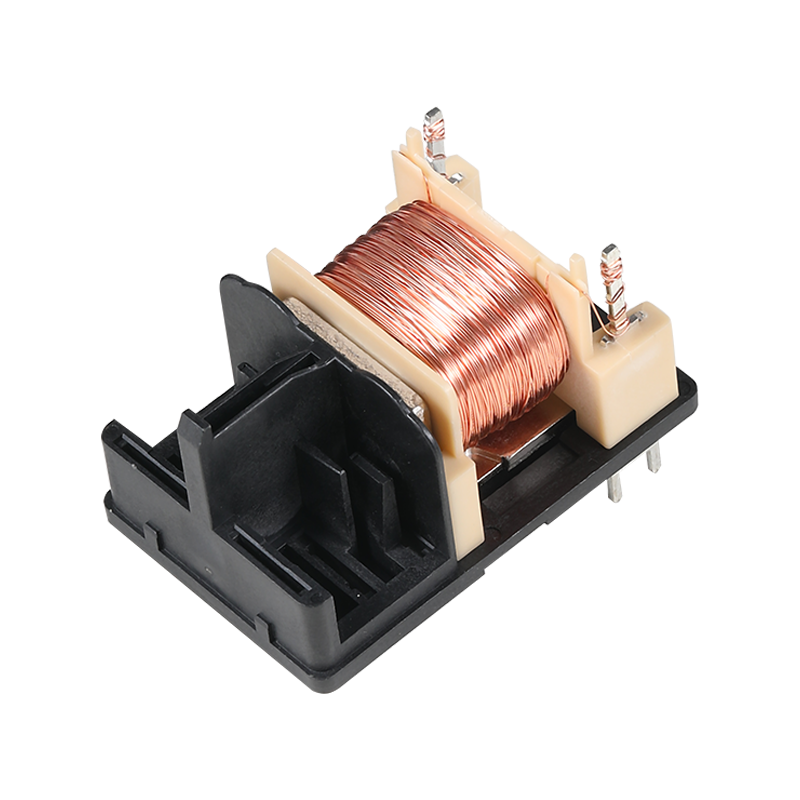
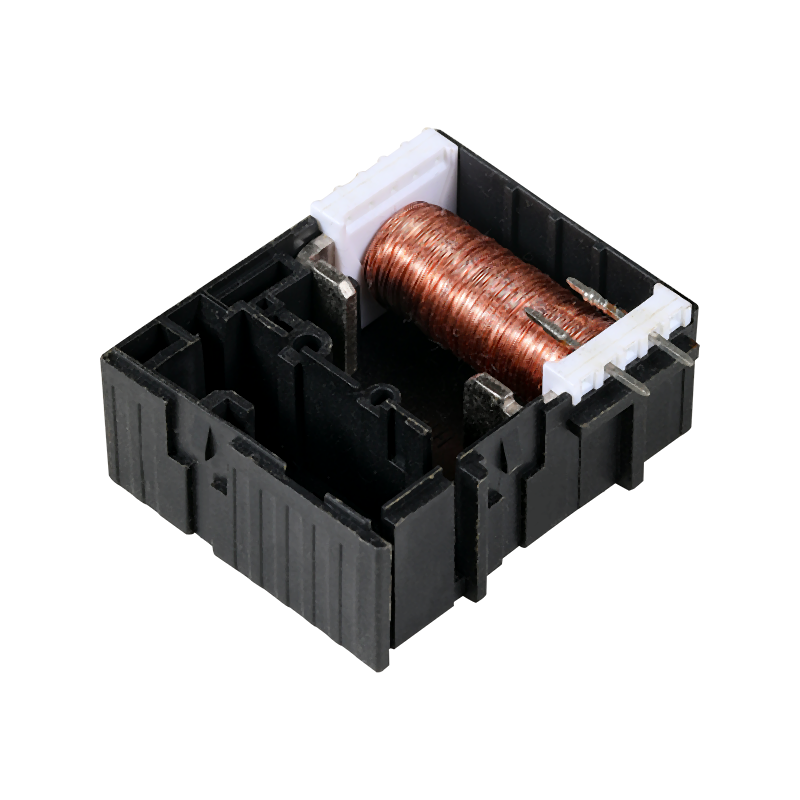
Relays are essential components in the world of electronics, serving as electromechanical switches that can make or break circuits when a specific condition is met. They are widely used in various applications due to their ability to control high power circuits with low power signals.
Current Monitor Relays are designed to monitor the flow of current in a circuit and trigger an action when the current exceeds or falls below a predetermined threshold. These relays are crucial in applications where it is necessary to protect circuits from overcurrent conditions that could pilot damage or failure. They are commonly used in power distribution systems, industrial automation, and electrical vehicles to ensure safety and reliability.
The operation of a Current Monitor Relay involves a coil that, when energized, creates a magnetic field. This field attracts a metal armature, which in turn closes or opens a set of contacts. These contacts can be used to switch high current loads on or off, depending on the current conditions. The relay's sensitivity and response time are critical factors in its performance, making it a versatile tool for managing electrical systems.
Circuit Board Relays, also known as PCB Relays, are designed to be mounted directly onto a printed circuit board (PCB). These relays are compact and offer a high level of integration with other electronic components. They are ideal for applications where space is at a premium, such as in consumer electronics, telecommunications, and computer systems.
The key advantage of Circuit Board Relays is their small form factor, which allows for dense packaging and efficient use of space on a PCB. They come in various configurations, including single-pole single-throw (SPST), single-pole double-throw (SPDT), and double-pole double-throw (DPDT), to suit different circuit requirements. These relays are also known for their fast switching times and low contact resistance, making them suitable for high-frequency applications.
Capacitor Start Relays are a specific type of relay used in single-phase induction motors, particularly in air conditioning and refrigeration systems. They are designed to provide a starting torque to the motor by introducing a phase shift in the current, which is achieved through the use of a capacitor.
The Capacitor Start Relay operates by initially connecting the motor's windings in parallel, allowing the motor to start with a high starting current. Once the motor reaches a certain speed, the relay then switches the windings to a series configuration, reducing the current and allowing the motor to run more efficiently. This type of relay is crucial for the proper functioning of the motor, ensuring smooth starts and preventing damage due to excessive starting current.
Relays offer several benefits in modern electronics, including:
Safety: They allow for the control of high power circuits with low power signals, reducing the risk of electric shock.
Isolation: They provide electrical isolation between the control circuit and the load, preventing potential damage to sensitive components.
Automation: Relays are a key component in automated systems, allowing for the remote control of machinery and processes.
Durability: They are designed to withstand a high number of operations, making them reliable for long-term use.
Versatility: Relays come in various types and configurations, allowing them to be tailored to specific applications.
In conclusion, relays such as Current Monitor Relays, Circuit Board Relays, and Capacitor Start Relays play a vital role in the operation and protection of electrical systems. They offer a range of benefits, from safety and isolation to automation and durability.
 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский