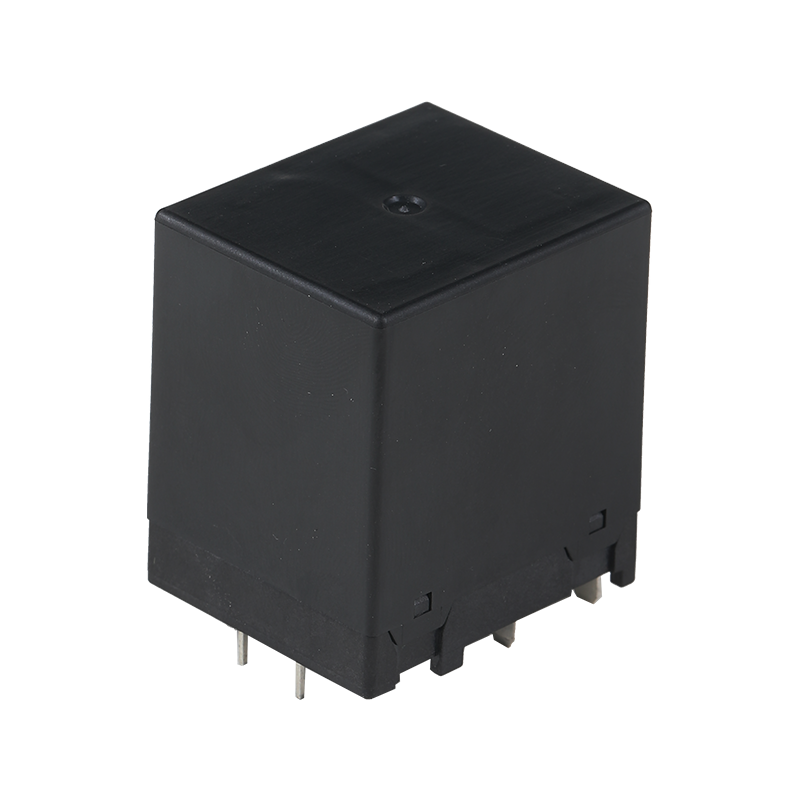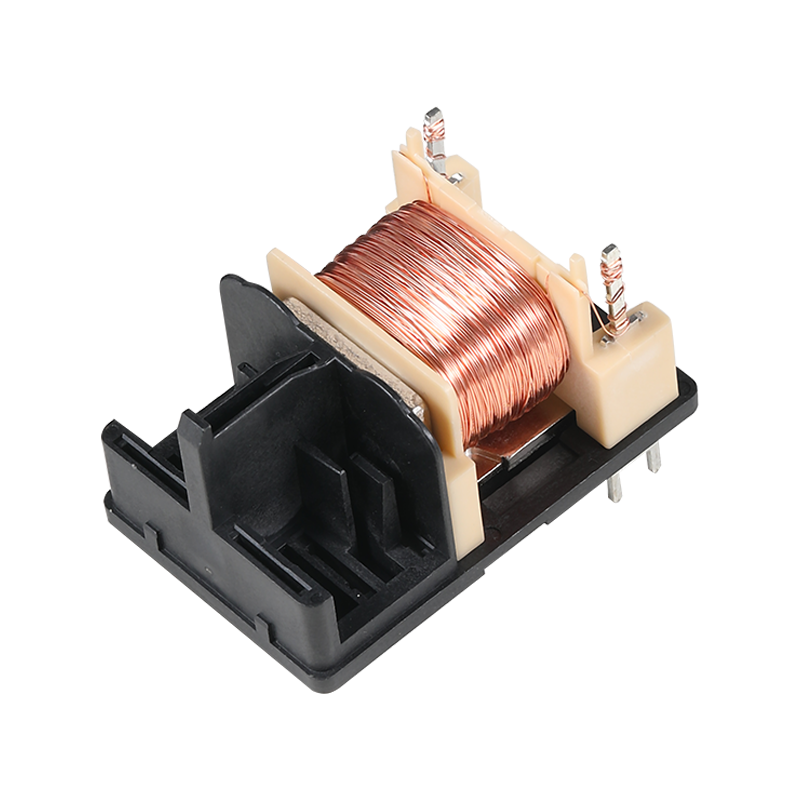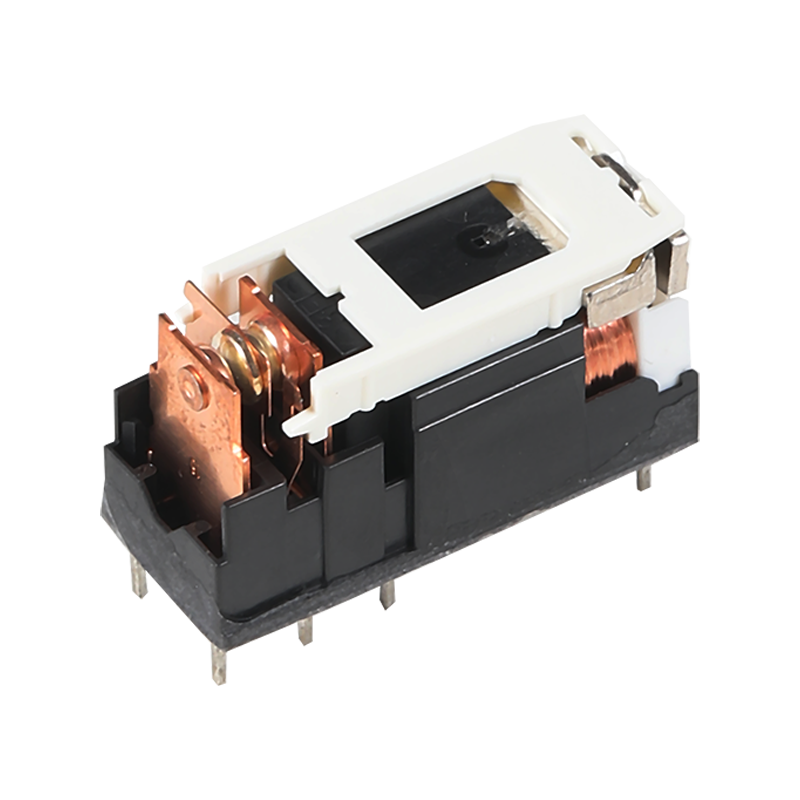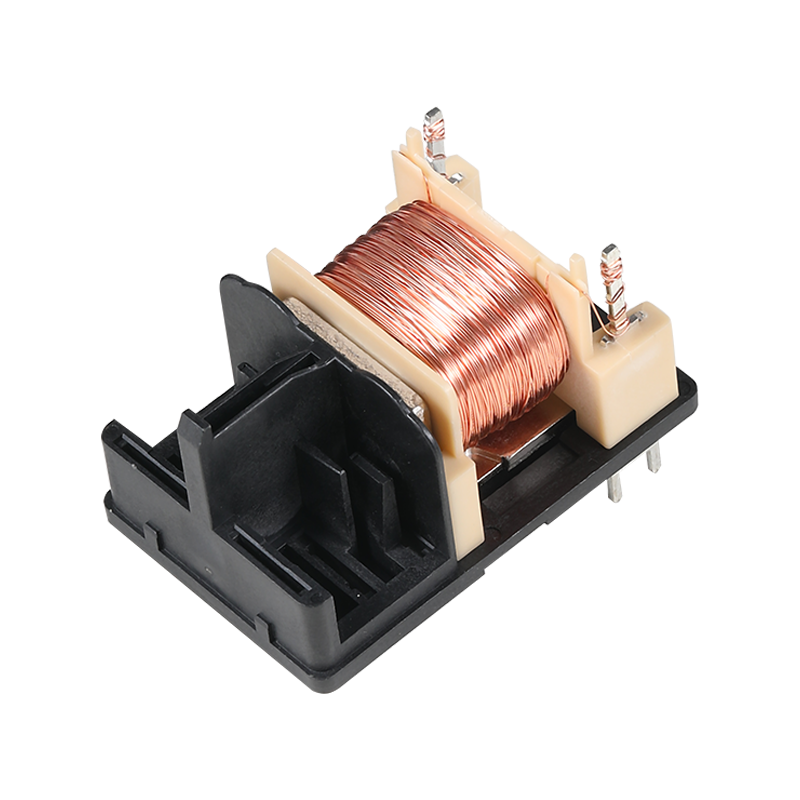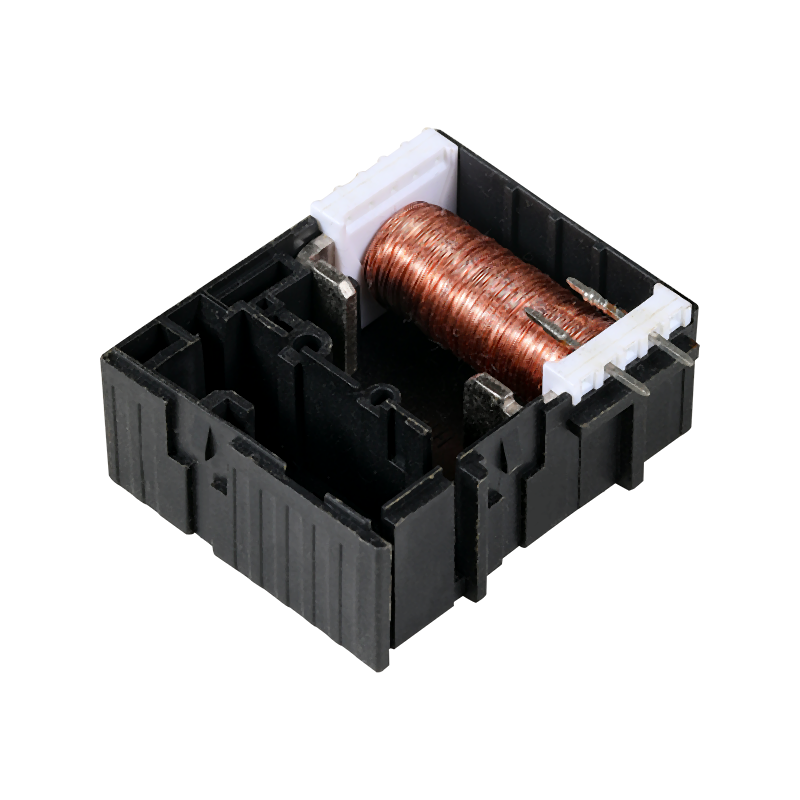
Relay switches are fundamental components in the field of industrial automation, providing a bridge between low-power control signals and high-power devices. These switches are essential for various applications, from simple on-off control to complex automation systems.
Industrial Relay Switches are designed to withstand the rigors of heavy-duty environments. They are built with robust construction to resist dust, moisture, and other contaminants commonly found in industrial settings. These relays are often used in applications where high current and voltage are involved, such as in motor control, power distribution, and heavy machinery. Industrial Relay Switches are known for their durability and long service life, which is crucial in environments where downtime can be costly.
Low Current Relay Switches, on the other hand, are specialized for applications that require the control of lower current loads. These relays are ideal for use in electronic circuits, telecommunications, and control systems where high precision and small power loss are desired. The low current draw of these relays makes them suitable for battery-operated devices and systems where energy conservation is a priority. They are also commonly found in home automation systems, where they can control lighting, security systems, and other smart home devices without drawing excessive power.
Micro Relay Switches are the smallest and more compact of the three, designed for space-constrained applications. They are often used in microcontroller-based systems, where size and weight are critical factors. Micro Relay Switches are found in a variety of applications, from automotive electronics to medical devices. Their small size allows them to be integrated into compact devices without sacrificing functionality. These relays are also known for their fast switching times and high reliability, making them a popular choice in applications where quick response times are essential.
All three types of relay switches operate on the same basic principle: they use an electromagnet to open or close a set of contacts, which in turn control the flow of current in a circuit. When an electrical signal is applied to the relay's control coil, the electromagnet creates a magnetic field that attracts a metal armature, causing the contacts to change state. This action can either complete or interrupt the circuit, allowing for remote control of devices.
The choice between Industrial, Low Current, and Micro Relay Switches depends on the specific requirements of the application. Factors such as the amount of current to be controlled, the environment in which the relay will operate, and the physical space available for the relay all play a role in determining the more appropriate type.
In terms of reliability, relay switches are known for their ability to switch high currents with small wear and tear. This is particularly important in industrial settings, where the relay may be called upon to switch thousands of times a day. The contacts in these relays are often made from materials that can withstand high temperatures and resist oxidation, further enhancing their longevity.
Maintenance is another area where relay switches excel. Since they have no moving parts other than the contacts and armature, they require small upkeep. This is in contrast to mechanical switches, which can wear out over time and require more frequent replacement.
In conclusion, relay switches are versatile components that serve a wide range of applications in industrial automation and beyond. Whether it's an Industrial Relay Switch for heavy-duty machinery, a Low Current Relay Switch for precision electronics, or a Micro Relay Switch for compact devices, these switches provide a reliable and efficient means of controlling electrical circuits.
 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский